Quantum Structures Facility (QSF)
Formerly known as the CNSI Nanostructures Cleanroom Facility (NCF), the Quantum Structures Facility (QSF) features cleanroom-based tool sets and processes that complement research in quantum materials and devices enabling unique capabilities in the pursuit of controlling and manipulating materials at the nanoscale.
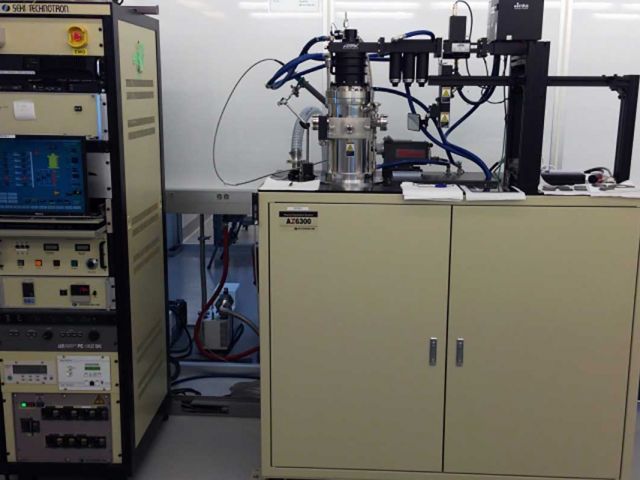
The facility houses a mix of traditional semi-conductor processing equipment, specialty deposition tools, a photoluminescent/Raman spectroscopy suite that includes a cryostat for cryogenic spectroscopy, and a Crystal Growth Facility that houses various types of crystal growth furnaces. An electro-optical characterization set up and probe station to test devices that is also available to UCSB users though a partnership with Hewlett Packard Enterprises (HPE).
Besides providing access to process and characterization equipment, the QSF is now one of the locations for the new NSF-funded Quantum Foundry with the addition of diamond specific etch, irradiation, and growth tools, as well as three dilution refrigeration units.
How-to Information
- Steps to Access the Quantum Structures Facility
-
- Initiate an Access Request (see inset).
- Contact QSF staff to get trained on the instrument.
- Provide additional billing/access forms (to be requested from academic/industry users external to UCSB).
- Apply to CNSI for electronic door access to the facility.
- QSF Staff will add you to the FBS reservation system.
- Acknowledging Support
-
Please remember to acknowledge CNSI resources in scientific publications and presentations by including this statement:
“The authors acknowledge the use of the Quantum Structures Facility within the California NanoSystems Institute, supported by the University of California, Santa Barbara and the University of California, Office of the President.”
For work related to the Quantum Foundry also include:
"This work is supported by the National Science Foundation through Enabling Quantum Leap: Convergent Accelerated Discovery Foundries for Quantum Materials Science, Engineering and Information (Q-AMASE-i) award number DMR-1906325."